 What is gastric bypass surgery?
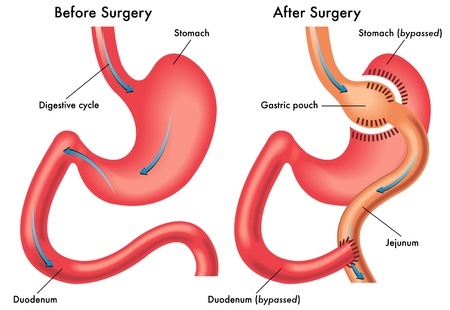
What is gastric bypass surgery?During gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon staples a small section of the stomach off from the rest of the stomach. The surgeon then connects the small intestines to the smaller section of the stomach. The result is that food passes from the mouth into the small stomach to the small intestines. Patients will have feel full after eating less food, helping them reduce their caloric intake.
To qualify for gastric bypass surgery, patients need to have a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher. For an example, a person who is six feet tall, needs to weigh around 300 lbs to have a BMI of 40. If the patient has a BMI of 35 or more and has one obesity-related health problem then he or she may also qualify for surgery, such as:
Patients who undergo the surgery are supposed to lose a significant amount of weight. This can lead to dramatic increases in health as well as self-confidence associated with losing weight. Doctors may only recommend that patients undergo the surgery after other options fail to produce sufficient weight loss.
Like all surgeries, gastric bypass surgery has its risks. One of the most dangerous is a blood clot traveling to the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism. Patients may suffer breathing problems, allergic reactions, infection, and other risks as well. It's important that patients discuss these and other risks with their doctor prior to the procedure. Another major drawback to the surgery is that the patient must change his or her life dramatically afterward. Of course, this might be a positive as patients can improve their health by adopting healthier dietary habits.
Because there is less stomach and food absorption after the surgery, patients may also be at increased risk of malnutrition and vitamin deficiency. Overeating, excessive drinking, and other actions may place the patient at risk of damaging their smaller stomach as well.
If something goes wrong in a gastric bypass surgery, the patient should explore the circumstances to determine the cause of the complications. Some are inherent risks of surgery, though if a healthcare professional caused the injuries, the patient may explore filing a medical malpractice case to recover damages.
The injured patient must prove that the professional violated the standard of care expected of other healthcare professionals. He or she must also establish that the malpractice led to the injury or complication and establish the damages related to the accident and injury.
Ryan, LLP in Cleveland is committed to protecting patients who have gastric bypass surgery and other procedures if medical negligence caused complications that resulted in injuries. Contact our office at 877-864-9495 or via our contact page to set up an appointment to speak with an attorney. About the author of this article: Thomas Ryan